 SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
SYSTEMS OF EQUATIONS in THREE VARIABLES
It is often desirable or even necessary to use more than one variable to model a situation in many fields. When this is the case, we write and solve a system of equations in order to answer questions about the situation.
If a system of linear equations has at least one solution, it is
consistent. If the system has no solutions, it is inconsistent. If
the system has an infinity number of solutions, it is dependent.
Otherwise it is independent.
A linear equation in three variables describes a plane and is an equation
equivalent to the equation
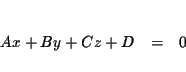
Problem 3.1e:
Solve the following system of equations for x, y and z:
| 7x+5y-3z | = | 16 | (1) |
| 3x-5y+2z | = | -8 | (2) |
| 5x+3y-7z | = | 0 | (3) |
Answer:
![]()
Solution:
We are going to show you how to solve this system of equations three
different ways:
1) Substitution,
2) Elimination
3) Matrices
SUBSTITUTION:
The process of substitution involves several steps:
Step 1: Solve for one of the variables in one of the equations. It
makes no difference which equation and which variable you choose. Let's
solve for x in equation (1).
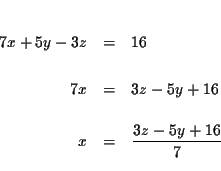
| 3x-5y+2z | = | -8 | |
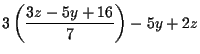 |
= | -8 | |
![$\displaystyle 7\left[ 3\left( \frac{3z-5y+16}{7}\right) -5y+2z\right]$](img6.gif) |
= | ||
| = | -56 | ||
| 9z-15y+48-35y+14z | = | -56 | |
| -50y+23z | = | -104 | |
| 50y-23z | = | 104 | (4) |
| 5x+3y-7z | = | 0 | |
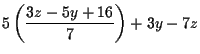 |
= | 0 | |
![$\displaystyle 7\left[ 5\left( \frac{3z-5y+16}{7}\right) +3y-7z\right]$](img10.gif) |
= | ||
| = | 0 | ||
| 15z-25y+80+21y-49z | = | 0 | |
| -4y-34z | = | -80 | |
| 2y+17z | = | 40 | (5) |
| 2y+17z | = | 40 | |
| y | = | 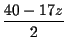 |
(6) |
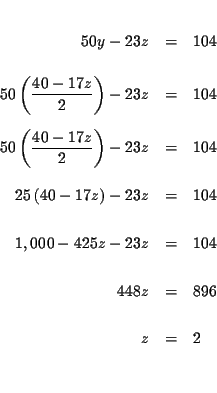
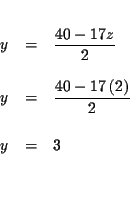
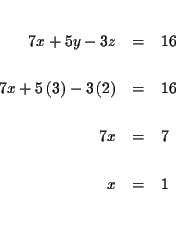
Step 8: Check the solutions:
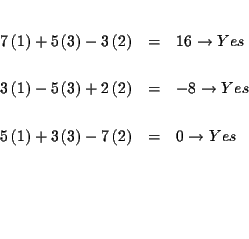
The process of elimination involves several steps: First you reduce three
equations to two equations with two variables, and then to one equation with
one variable.
Step 1: Decide which variable you will eliminate. It makes no
difference which one you choose. Let us eliminate y first.
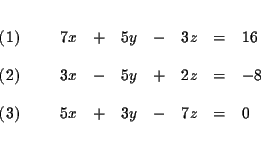
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
\left[ Equation\ 1\right] +\left[ Equation\ 2\right] &=...
... &=&\left[
\begin{array}{c}
Equation\ 5
\end{array}
\right]
\end{eqnarray*}](img21.gif)
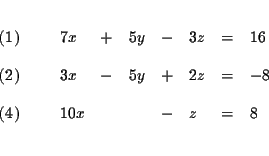
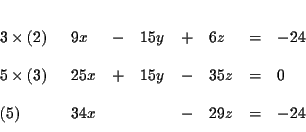
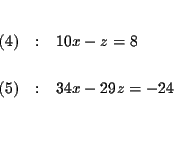
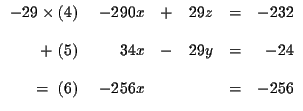
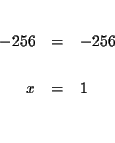
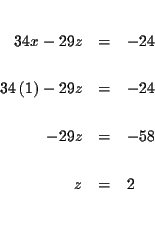
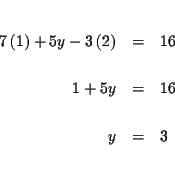
MATRICES:
The process of using matrices is essentially a shortcut of the process of
elimination. Each row of the matrix represents an equation and each column
represents coefficients of one of the variables.
Step 1:
Create a three-row by four-column matrix using coefficients and the constant
of each equation.
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...& \\
5 & & 3 & & -7 & \vert & 0
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img29.gif)
The vertical lines in the matrix stands for the equal signs between both
sides of each equation. The first column contains the coefficients of x, the
second column contains the coefficients of y, the third column contains the
coefficients of z, and the last column contains the constants.
We want to convert the original matrix
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...& \\
5 & & 3 & & -7 & \vert & 0
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img29.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
... & \\
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & c
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img30.gif)
Step 2: We work with column 1 first. Multiply Row 1 by
![]() to form a new Row 1.
to form a new Row 1.
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
\frac{1}{7}\left[ Row\ 1\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 1\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img32.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...& \\
5 & & 3 & & -7 & \vert & 0
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img33.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-3\left[ Row\ 1\right] +\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ ...
...ht] +\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 3\right]
\\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img34.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...c{34}{7} & \vert & -\dfrac{80}{7}
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img35.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-\frac{7}{50}\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 2\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img37.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...c{34}{7} & \vert & -\dfrac{80}{7}
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img38.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-\frac{5}{7}\left[ Row\ 2\right] +\left[ Row\ 1\right] ...
...ht] +\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\
3\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img41.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
...75} & \vert & -\dfrac{1,792}{175}
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img42.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
-\dfrac{175}{896}\left[ Row\ 3\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\ 3\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img44.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
... & \\
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & 2
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img45.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
\frac{1}{10}\left[ Row\ 3\right] +\left[ Row\ 1\right] ...
...ht] +\left[ Row\ 2\right] &=&\left[ New\ Row\
2\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img48.gif)
![\begin{eqnarray*}&& \\
&&
\begin{array}{r}
(1) \\
\\
(2) \\
\\
(3)
...
... & \\
0 & & 0 & & 1 & \vert & 2
\end{array}
\right] \\
&&
\end{eqnarray*}](img49.gif)
If you would like to go back to the problem page, click on Problem.
If you would like to review the solution to the next problem, click on Problem
If you would like to return to the beginning of the three by three system of equations, click on Example.
This site was built to accommodate the needs of students. The topics and problems are what
students ask for. We ask students to help in the editing so that future viewers will access
a cleaner site. If you feel that some of the material in this section is ambiguous or needs
more clarification, or if you find a mistake, please let us know by e-mail at sosmath.com.

Do you need more help? Please post your question on our S.O.S. Mathematics CyberBoard.

Author: Nancy Marcus